Variant Trifurcation of the Ulnar Nerve in Guyon’s Canal of the Human Wrist: Case report
Abstract
During routine dissection of the right hand of a 52-year-old Asian descent male cadaver in the Department of Anatomy at Jazan University-Faculty of Medicine, we observed an anatomical variation of the ulnar nerve (UN). There was a trifurcation of the nerve in the ulnar tunnel proximal to the pisiform bone. An awareness of such variation may be of great clinical importance despite the presence of trifurcation of the ulnar nerve, which does not usually cause symptoms but becomes important in the evaluation of entrapment neuropathy and during surgical and orthopedic interventions
Author Contributions
Academic Editor: Abdelmonem Awad Mustafa Hegazy, Professor and Former Chairman of Anatomy and Embryology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt.
Checked for plagiarism: Yes
Review by: Single-blind
Copyright © 2021 Tagreed Fathi Ali, et al.
 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Citation:
Introduction
The ulnar nerve is the continuation of the medial cord of the brachial plexus (C8, T1) within the axilla region. The nerve first descends on the medial side of the upper arm to the level of the mid humerus, then it deviates posteriorly to enter the posterior compartment of the arm and follows the medial head of the triceps posterior to the medial epicondyle to the cubital tunnel. Then it descends to enter the forearm between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle, then in between this muscle and the flexor digitorum profundus muscle 1. It gives muscular branches to the medial half of the flexor digitourum superficialis and flexor carpi ulnaris in the forearm and continues to enter the hand by passing superficial to the flexor retinaculum inside the ulnar tunnel (Guyon’s canal) 2.
The Guyon’s Canal, is a fibro-osseous tunnel, 4– 4.5 cm in length, located on the medial side of the wrist, extending from the pisiform bone medially to the hook of the hamate bone laterally. The anterior wall is formed by the palmar carpal ligament proximally and adipose tissue distally, while its posterior wall is formed by the transverse carpal ligament 3. Within the tunnel, and just distal to the pisiform bone, the nerve bifurcates into a superficial terminal branch that supplies sensation to the small finger and the ulnar half of the ring finger, and the deep palmar branch disappears into the hypothenar muscles where it is supplied and it continues into the deep palmar space to innervate the deep muscles of the hand 2. Ulnar nerve variations in the wrist are rare, although they may be of great clinical significance during wrist surgical interventions 4.
Case Report
During routine dissection of the right hand of a 52-year-old Asian descent male cadaver in the Department of Anatomy at Jazan University Faculty of Medicine, this cadaver displayed no signs of injury, fractures, or musculoskeletal disease.
We observed an interesting case of low trifurcation of the ulnar nerve. The ulnar nerve enters the hand superficial to the flexor retinaculum, deep to the palmar carpal ligament and medial to the ulnar artery inside the ulnar tunnel (Guyon’s canal), six mm proximal to the distal end of the pisiform bone, and is divided into three terminal branches; a deep branch and two superficial branches; a common palmar digital nerve and a medial (ulnar) palmar digital nerve. The deep branch continues to enter through the pisohamate hiatus to supply the hypothenar and deep muscles of the hand, while the common palmar digital nerve branches distally into terminal digital branches (to digits 4 and 5) and a medial (ulnar) palmar digital nerve (to digit 5). Figure 1 (Figure 2)
After the ulnar nerve was identified in the right hand, it was traced to the left hand. The branching pattern was the bifurcation pattern as it branched into two terminal branches; the superficial sensory branch and the deep motor branch. Figure 3
Figure 1.Photograph of the right-hand showing trifurcation pattern of the ulnar nerve UA, ulnar artery; UN,ulnar nerve; P, pisiform bone.
Figure 2.Photograph of the right-hand showing the three branches of the ulnar nerve. P, pisiform bone.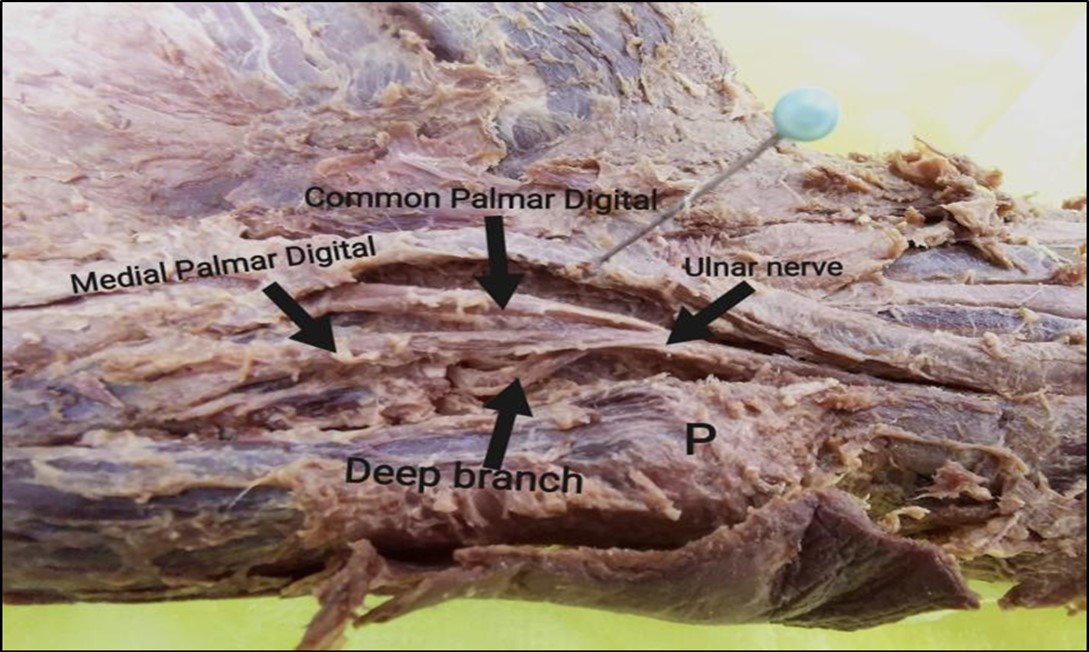
Figure 3.Photograph of the left-hand showing bifurcation pattern of the ulnar nerve. UA, ulnar artery; UN,ulnar nerve.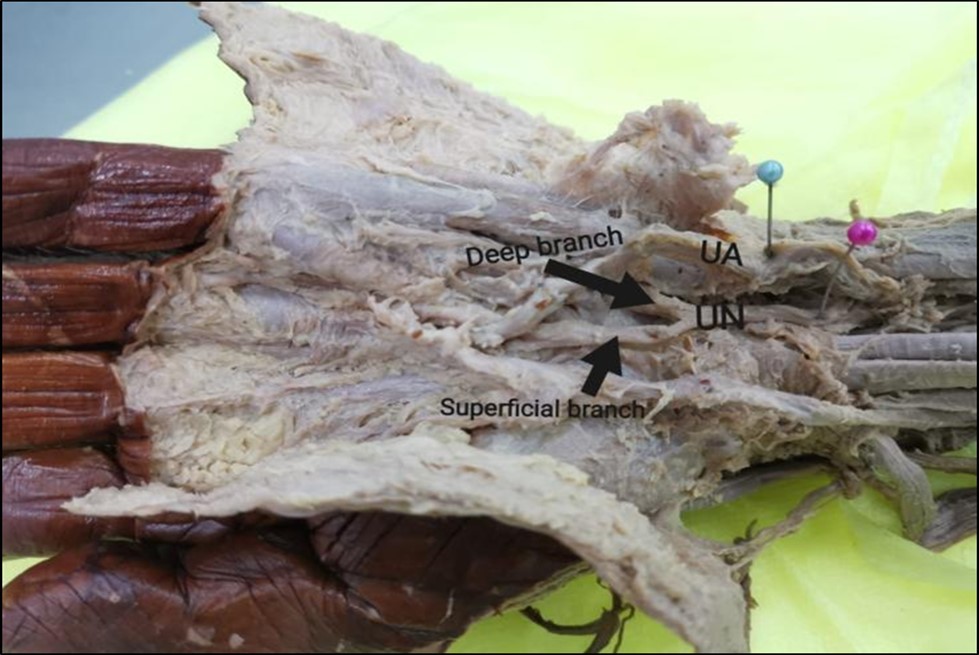
Discussion
Variations in the branching pattern of the ulnar nerve have been seen in cadaveric dissections 5, 6 and during clinical practice 7, 8. The common presentation of the ulnar nerve branching pattern in the Guyon’s canal is bifurcation into two branches as reported by Depukat et al. 5. It showed that the UN most commonly branched into two branches; a superficial sensory branch and a deep motor branch in 85% of cases.
The trifurcation of the ulnar nerve seen in the current study was the same as what was seen in the type 2 branching pattern of the ulnar nerve reported by Murata et al 9 and Verhiel et al 10. The incidence was 9% and 22%, respectively. The ulnar nerve follows the trifurcated type with one deep branch and two superficial branches inside the ulnar tunnel. In this case, the ulnar nerve represents the low trifurcated pattern, as it is divided inside the ulnar tunnel and the dorsal sensory branch, which originates normally proximal to the wrist, turns back to enter the dorso-ulnar side of the distal forearm to supply sensation to the skin of the dorsum of the hand as well as the dorsal aspects of the little and ring fingers. A high trifurcation pattern was reported in a case report by Al-Qattan et al. 7. The ulnar nerve is found trifurcated in the middle of the forearm into a dorsal sensory nerve, an intermediate motor, and a radial volar sensory branch.
The clinical importance of the ulnar nerve pathway and its variations in the wrist mostly related to its entrapment in the Guyon’s canal. There are three zones that were described to help localization of the lesion of the ulnar nerve in the wrist 11, Zone1 proximal to or in the ulnar tunnel before it bifurcates to superficial and deep branches, both motor and sensory branches affected. Zone 2 distal to Zone I, injury in this zone affects only the motor branch result in paralysis of the intrinsic muscles and/or the hypothenar muscles with sensory intact. Zone 3 radial to Zone 2. It surrounds the superficial branch only. A lesion in this zone leads to loss of sensation of digit 5, the medial half of digit 4, and hypothenar eminence. Due to the ulnar nerve topography variations as incidence of trifurcations in the current case, patients may present with different zone patterns. We would like to suggest, as Depukat et al. suggest, exploring the whole space from lateral to medial, or starting from Zone 3 and extending to Zone 1 4.
Variations of the ulnar nerve pathway in the wrist in the anatomical classic textbooks are not well described. Further studies may add important data for anatomical and clinical practice.
Conclusion
Knowledge of UN variations would help surgeons to understand and diagnose different symptoms that cannot be explained by the normal anatomy of the nerve. Also, it can help in preserving these variant branches during surgical procedures of the hand, such as carpal tunnel release, exploration of the ulnar tunnel, palmar fasciectomy, and different hand surgeries.
References
- 1.Sato T, Hirano Y, Sato N, Sato K. (2018) A rare anatomical variation of the course of the ulnar nerve. , Int J Anat Var 11(1), 35.
- 2.Sallomi D, Janzen D L, Munk P L, Connell D G, Tirman P F. (1998) Muscle denervation patterns in upper limb nerve injuries: MR imaging findings and anatomic basis. American journal of roentgenology. 171(3), 779-84.
- 3.Klimek-Piotrowska W, Mizia E, Depukat P, Kłosiński M, Dzikowska M et al. (2014) Anatomy of Guyon’s canal—a systematic review. Folia Medica Cracoviensia.
- 4.Dodds G A, Hale D, Jackson W T. (1990) Incidence of anatomic variants in Guyon's canal. The Journal of hand surgery. 15(2), 352-5.
- 5.Depukat P, Henry B M, Popieluszko P, Roy J, Mizia E et al. (2017) Anatomical variability and histological structure of the ulnar nerve in the Guyon’s canal. Archives of orthopaedic and trauma surgery. 137(2), 277-83.
- 6.Ghabriel M N, Makar P H. (2011) Anatomical variations in the ulnar nerve and hypothenar muscles. , Int J Anat Var 4, 131-133.
- 7.Al-Qattan M M, Alqahtani A, Al-Zahrani A. (2018) High trifurcation of the ulnar nerve with the volar sensory branch entering the hand superficial and radial to the Guyon’s canal: A case report. International journal of surgery case reports. 51, 33-6.
- 8.Zeiss J, Jakab E, Khimji T, Imbriglia J. (1992) The ulnar tunnel at the wrist (Guyon's canal): normal MR anatomy and variants. American journal of roentgenology. 158(5), 1081-5.
- 9.Murata K, Tamai M, Gupta A. (2004) Anatomic study of variations of hypothenar muscles and arborization patterns of the ulnar nerve in the hand. The Journal of hand surgery. 29(3), 500-9.
